Your Cranial duodenal flexure dog images are ready. Cranial duodenal flexure dog are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Cranial duodenal flexure dog files here. Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for cranial duodenal flexure dog images information linked to the cranial duodenal flexure dog topic, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website always provides you with hints for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Cranial Duodenal Flexure Dog. After the distal duodenal flexure the. The adjacent duodenal lymph node was also enlarged. In dogs without gastrointestinal disease there were 628 of gastrointestinal segments serosa to serosa and 777 of gastrointestinal walls serosa to mucosa visualized. In this module of the animal atlas vet-Anatomy is displayed the cross-sectional labeled anatomy of the canine abdominal cavity and the pelvis on a Computed Tomography CT and on 3D images of the abdomen of the dog.
 Anatomy Week 11 Material Block Week 12 Flashcards Chegg Com From chegg.com
Anatomy Week 11 Material Block Week 12 Flashcards Chegg Com From chegg.com
The caudal flexure passes caudal to the root of the mesentery so that the ascending duodenum is then to the left of the root of the mesentery. The area of the cranial duodenal flexure the first part of the duodenum was also abnormal. Small Intestines of the Dog. Sie markiert den Übergang von der Pars descendens des Zwölffingerdarms in die Pars horizontalis inferior. Secretory Brunner glands and annular mucosal folds are features of the human proximal duodenum but are not present in dogs and cats. The adjacent duodenal lymph node was also enlarged.
Its parietal surface faces cranioventrally toward the liver and its.
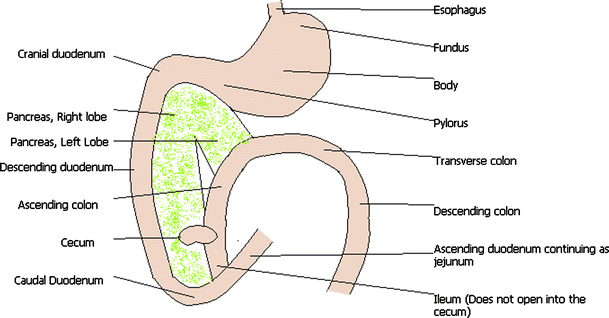
CT images are from a healthy 6-year-old castrated male dog. The descending duodenum runs dorsally and caudally along the right abdominal wall before turning medially at the caudal duodenal flexure. In dogs the antimesenteric side of the duodenum is marked by a line of whitish mucosal depressions signifying the presence of specialized lymphoid areas the Peyer patches see Figure 57-2 C. The duodenum passes cranially and dorsally for a short distance as the cranial part then it turns caudally to form the cranial duodenal flexure. This blood carrying the products of digestion enters the liver. The duodenum is about 25cm long in canine species.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Definition Die Flexura duodeni inferior ist eine rechts von der Medianebene gelegene Krümmung Flexur des Zwölffingerdarms Duodenum. The health of these dogs including fecal consistency had been monitored daily and necropsy examinations performed while harvesting the duodenal biopsies were unremarkable. In this module of the animal atlas vet-Anatomy is displayed the cross-sectional labeled anatomy of the canine abdominal cavity and the pelvis on a Computed Tomography CT and on 3D images of the abdomen of the dog. The canine duodenum is the thickest portion of the small intestine in the dog and normally has a thicker mucosal layer than the jejunum. An intercostal right-sided approach may be necessary to identify the cranial duodenal flexure in a dog.
 Source: veteriankey.com
Source: veteriankey.com
In dogs without gastrointestinal disease there were 628 of gastrointestinal segments serosa to serosa and 777 of gastrointestinal walls serosa to mucosa visualized. The duodenum runs cranially and laterally from the pylorus and then turns caudally forming the cranial duodenal flexure. CT images are from a healthy 6-year-old castrated male dog. This blood carrying the products of digestion enters the liver. The duodenum courses caudally along the right abdominal wall.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
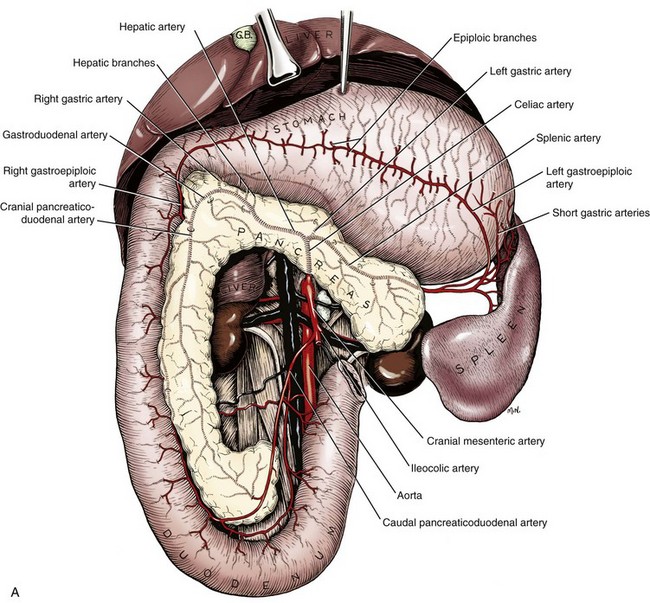
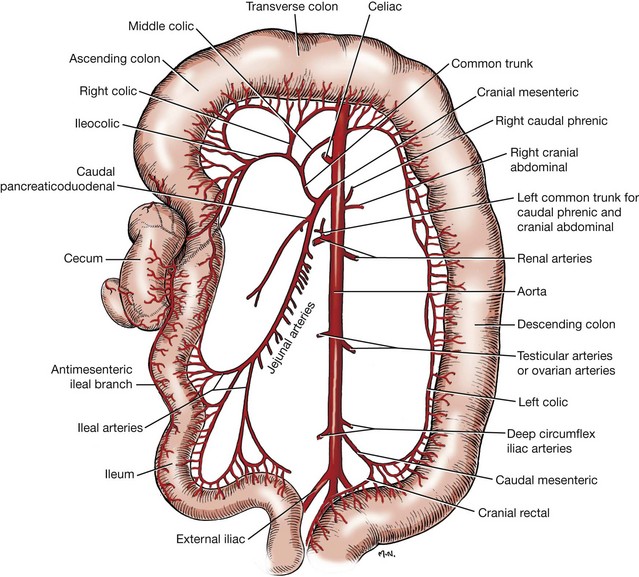
The canine duodenum is the thickest portion of the small intestine in the dog and normally has a thicker mucosal layer than the jejunum. An intercostal right-sided approach may be necessary to identify the cranial duodenal flexure in a dog. The duodenum receives blood from the coeliac artery and the cranial mesenteric artery. In dogs the antimesenteric side of the duodenum is marked by a line of whitish mucosal depressions signifying the presence of specialized lymphoid areas the Peyer patches see Figure 57-2 C. Both are branches of the aorta.
 Source: scialert.net
Source: scialert.net
Wall layering on postcontrast images was seen in 218 of gastrointestinal segments. The canine duodenum is the thickest portion of the small intestine in the dog and normally has a thicker mucosal layer than the jejunum. Small Intestines of the Dog. The liver is located in the cranial aspect of the abdomen between the diaphragm which delineates its cranial border and the stomach right kidney and cranial portion of the duodenum which define the caudal extent. This is an opening caudomedial to the caudate lobe of the liver at the level of the cranial duodenal flexure which will be identified later in this lab after observing the lobes of the liver.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
This blood carrying the products of digestion enters the liver. In dogs without gastrointestinal disease there were 628 of gastrointestinal segments serosa to serosa and 777 of gastrointestinal walls serosa to mucosa visualized. From the stomach B food travels into the duodenum C. This first curvebend in the duodenum is called the cranial duodenal flexure. The duodenum receives blood from the coeliac artery and the cranial mesenteric artery.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
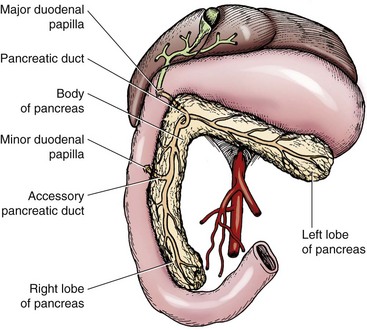
This blood carrying the products of digestion enters the liver. Small Intestines of the Dog. Larger duct- accessory pancreatic minor duct into duodenum at minor or caudal duodenal papilla Small duct not always present- pancreatic major duct opens at major or cranial duodenal papilla in common with bile duct. Wall layering on postcontrast images was seen in 218 of gastrointestinal segments. CT images are from a healthy 6-year-old castrated male dog.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
In dogs the antimesenteric side of the duodenum is marked by a line of whitish mucosal depressions signifying the presence of specialized lymphoid areas the Peyer patches see Figure 57-2 C. The duodenum begins at the pylorus and then curves to the right to course caudally. The flexure is held against the caudal surface of the right liver lobes by the hepatoduodenal ligament. Definition Die Flexura duodeni inferior ist eine rechts von der Medianebene gelegene Krümmung Flexur des Zwölffingerdarms Duodenum. Part B from Evans HE de Lahunta A.

The liver is located in the cranial aspect of the abdomen between the diaphragm which delineates its cranial border and the stomach right kidney and cranial portion of the duodenum which define the caudal extent. Using your fingers gently peel the greater omentum away from the abdominal organs and reflect it cranially to continue identifying structures within the abdomen. There was significant association between gastrointestinal diameter and wall thickness. The cranial part attached to the liver by the hepatoduodenal ligament. After the distal duodenal flexure the.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The liver is nearly entirely within the costal arch with the caudal ventral border composed of the left lateral liver lobe in the dog extending just. The duodenum passes cranially and dorsally for a short distance as the cranial part then it turns caudally to form the cranial duodenal flexure. It begins at the pylorus to the right of the median plane. The health of these dogs including fecal consistency had been monitored daily and necropsy examinations performed while harvesting the duodenal biopsies were unremarkable. Bauch- und Beckeneingeweide Wichtiger Hinweis zu diesem Artikel.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
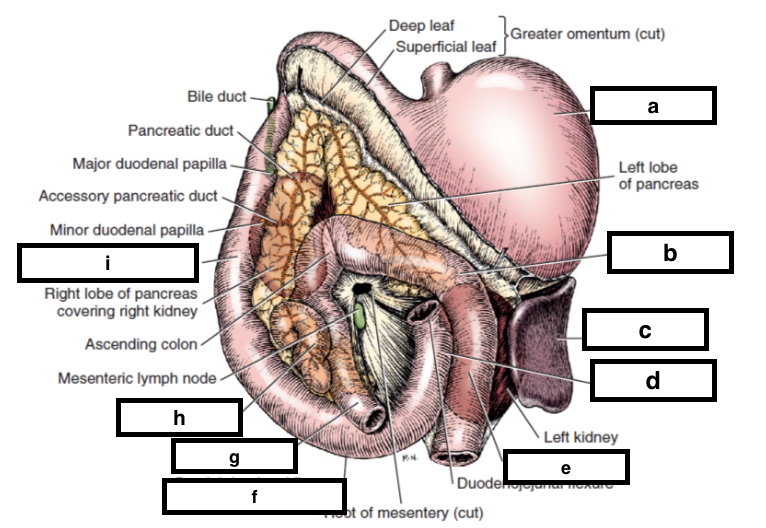
Larger duct- accessory pancreatic minor duct into duodenum at minor or caudal duodenal papilla Small duct not always present- pancreatic major duct opens at major or cranial duodenal papilla in common with bile duct. This blood carrying the products of digestion enters the liver. CT images are available in 3 different planes transverse sagittal. Oblique view of the cranial duodenal flexure in a dog with a benign ulcer subsequent to NSAID and glucocorticoid treatment. Control tissues comprised endoscopic biopsies collected from the cranial duodenal flexure of 10 healthy Beagle dogs immediately after euthanasia undertaken for reasons unrelated to this study.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Gastric fundus gastric body gastric pylorus gastric pyloric antrum duodenal cranial flexure jejunum and ascending colon and between patient weight and gastrointestinal diameter in cranial duodenal flexure descending duodenum transverse. After the distal duodenal flexure the. Cranial duodenal flexure descending part caudal duodenal flexure ascending part duodenojejunal flexure jejunum mesenteric lymph nodes in mesojejunum mesoileum ileum ileal orifice ileocolic orifice Large Intestines. CT images are from a healthy 6-year-old castrated male dog. Wall layering on postcontrast images was seen in 218 of gastrointestinal segments.
 Source: veteriankey.com
Source: veteriankey.com
The liver is nearly entirely within the costal arch with the caudal ventral border composed of the left lateral liver lobe in the dog extending just. Cra- nial cranial duodenal flexure descending caudal duodenal flexure transverse and ascending portions. The liver is nearly entirely within the costal arch with the caudal ventral border composed of the left lateral liver lobe in the dog extending just. Cranial duodenal flexure descending part caudal duodenal flexure ascending part duodenojejunal flexure jejunum mesenteric lymph nodes in mesojejunum mesoileum ileum ileal orifice ileocolic orifice Large Intestines. In dogs without gastrointestinal disease there were 628 of gastrointestinal segments serosa to serosa and 777 of gastrointestinal walls serosa to mucosa visualized.

Part B from Evans HE de Lahunta A. This blood carrying the products of digestion enters the liver. Cra- nial cranial duodenal flexure descending caudal duodenal flexure transverse and ascending portions. The duodenum receives blood from the coeliac artery and the cranial mesenteric artery. The liver is nearly entirely within the costal arch with the caudal ventral border composed of the left lateral liver lobe in the dog extending just.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Using your fingers gently peel the greater omentum away from the abdominal organs and reflect it cranially to continue identifying structures within the abdomen. An intercostal right-sided approach may be necessary to identify the cranial duodenal flexure in a dog. The flexure is held against the caudal surface of the right liver lobes by the hepatoduodenal ligament. This is the descending part of the duodenum. This is an opening caudomedial to the caudate lobe of the liver at the level of the cranial duodenal flexure which will be identified later in this lab after observing the lobes of the liver.
 Source: veteriankey.com
Source: veteriankey.com
The descending duodenum runs dorsally and caudally along the right abdominal wall before turning medially at the caudal duodenal flexure. Readily identifiable landmarks that were used were the portal vein and caudal vena cava spleen cranial duodenal flexure left kidney and aorta as described previously. Larger duct- accessory pancreatic minor duct into duodenum at minor or caudal duodenal papilla Small duct not always present- pancreatic major duct opens at major or cranial duodenal papilla in common with bile duct. Secretory Brunner glands and annular mucosal folds are features of the human proximal duodenum but are not present in dogs and cats. The liver is located in the cranial aspect of the abdomen between the diaphragm which delineates its cranial border and the stomach right kidney and cranial portion of the duodenum which define the caudal extent.
 Source: veteriankey.com
Source: veteriankey.com
Cra- nial cranial duodenal flexure descending caudal duodenal flexure transverse and ascending portions. Roger couldnt be sure at the time but there did appear to be a hyperechoic fragment of foreign material within the wall at this point. The health of these dogs including fecal consistency had been monitored daily and necropsy examinations performed while harvesting the duodenal biopsies were unremarkable. There was significant association between gastrointestinal diameter and wall thickness. After the distal duodenal flexure the.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The adjacent duodenal lymph node was also enlarged. The descending duodenum runs dorsally and caudally along the right abdominal wall before turning medially at the caudal duodenal flexure. This blood carrying the products of digestion enters the liver. Cecum cecocolic orifice dog indistinct in cat colon ascending transverse descending palpate. The flexure is held against the caudal surface of the right liver lobes by the hepatoduodenal ligament.
 Source: sonopath.com
Source: sonopath.com
An intercostal right-sided approach may be necessary to identify the cranial duodenal flexure in a dog. Small Intestines of the Dog. The duodenum is divided into four portions and two flexures. There was significant association between weight and gastrointestinal wall thickness in the following regions. Larger duct- accessory pancreatic minor duct into duodenum at minor or caudal duodenal papilla Small duct not always present- pancreatic major duct opens at major or cranial duodenal papilla in common with bile duct.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title cranial duodenal flexure dog by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






